Java try-catch块
Java try-catch块
Java try块
Java
try 块用于封装可能引发异常的代码。它必须在方法内使用。
如果try块的特定语句发生异常,则其余的块代码将不执行。因此,建议不要将代码保留在不会引发异常的try块中。
Java try块之后必须是catch或finally块。
Java try-catch的语法
try{
//code that may throw an exception
}catch(Exception_class_Name ref){}
try-finally块的语法
try{
////code that may throw an exception
}finally{}
Java catch块
Java catch块用于通过在参数中声明异常的类型来处理Exception。声明的异常必须是父类异常(即Exception)或生成的异常类型。但是,好的方法是声明生成的异常类型。
只能在try块之后使用catch块。您可以将多个catch块与一个try块一起使用。
没有异常处理的问题
如果我们不使用try-catch块,让我们尝试理解问题。
示例1
public class trycatchExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int data=50/0; //may throw exception
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
}
输出:
线程"主"中的异常java.lang.ArithmeticException:
如上例所示,未执行
其余代码(在这种情况下,不会显示
其余代码语句)。
异常后可能有100行代码。因此,异常后的所有代码都不会执行。
通过异常处理的解决方案
让我们看看通过java try-catch块解决上述问题的方法。
示例2
public
class trycatchExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int data=50/0; //may throw exception
}
//handling the exception
catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
}
输出:
java.lang.ArithmeticException:
其余代码
现在,如上例所示,执行
其余代码,即,打印
其余代码语句。
示例3
在此示例中,我们还将代码保留在不会引发异常的try块中。
public class trycatchExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int data=50/0; //may throw exception
// if exception occurs, the remaining statement will not exceute
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
// handling the exception
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
java.lang.ArithmeticException:
在这里,我们可以看到,如果try块中发生异常,则其余的块代码将不会执行。
示例4
在这里,我们使用父类异常处理异常。
public class trycatchExample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int data=50/0; //may throw exception
}
// handling the exception by using Exception class
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
}
输出:
java.lang.ArithmeticException:
其余代码
示例5
让我们看一个在异常时打印自定义消息的示例。
public class trycatchExample5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int data=50/0; //may throw exception
}
// handling the exception
catch(Exception e)
{
// displaying the custom message
System.out.println("Can't divided by zero");
}
}
}
输出:
示例6
让我们看一个在catch代码块中解决异常的示例。
public class trycatchExample6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=50;
int j=0;
int data;
try
{
data=i/j; //may throw exception
}
// handling the exception
catch(Exception e)
{
// resolving the exception in catch block
System.out.println(i/(j+2));
}
}
}
输出:
示例7
在此示例中,我们还将try代码与try代码一起包含在catch代码块中。
public class trycatchExample7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int data1=50/0; //may throw exception
}
// handling the exception
catch(Exception e)
{
// generating the exception in catch block
int data2=50/0; //may throw exception
}
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
}
输出:
线程"主"中的异常java.lang.ArithmeticException:
在这里,我们可以看到catch块不包含异常代码。因此,请将异常代码包含在try块中,并仅使用catch块来处理异常。
示例8
在此示例中,我们处理生成的异常(算术异常)和其他类型的异常类(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)。
public class trycatchExample8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int data=50/0; //may throw exception
}
// try to handle the ArithmeticException using ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
}
输出:
线程"主"中的异常java.lang.ArithmeticException:
示例9
让我们看一个示例来处理另一个未经检查的异常。
public class trycatchExample9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int arr[]= {1,3,5,7};
System.out.println(arr[10]); //may throw exception
}
// handling the array exception
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("rest of the code");
}
}
输出:
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10
其余代码
示例10
让我们看一个处理已检查异常的示例。
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class trycatchExample10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintWriter pw;
try {
pw = new PrintWriter("jtp.txt"); //may throw exception
pw.println("saved");
}
// providing the checked exception handler
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("File saved successfully");
}
}
输出:
java try-catch块的内部工作
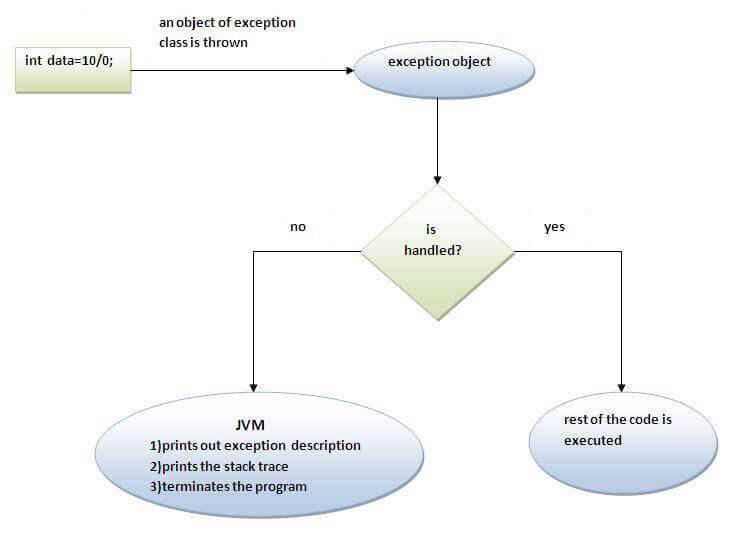
JVM首先检查是否处理了异常。如果未处理异常,则JVM提供一个默认的异常处理程序,该处理程序执行以下任务:
打印出异常描述。
打印堆栈跟踪记录(发生异常的方法的层次结构)。
导致程序终止。
但是,如果异常是由应用程序程序员处理的,则将维持应用程序的正常流程,即执行其余代码。
