如何在Java中创建对象
如何使用Java创建对象
对象是OOPs语言。在
Java 中,如果不创建
对象,我们将无法执行任何程序。有多种方法可以
在Java中创建对象 ,在本节中进行讨论,还学习
如何用Java创建对象。
Java 提供了五种创建对象的方法。
使用new关键字
使用 clone()方法
使用 Class 类的 newInstance()方法
使用 Constructor 类的 newInstance()方法
使用反序列化
使用新关键字
使用
new 关键字是创建类的对象或实例的最流行的方法。当我们使用new关键字创建类的实例时,它为新创建的
对象分配内存(堆),并将该对象的
引用返回到该内存。 new关键字也用于创建数组。创建对象的语法是:
ClassName object = new ClassName();
我们创建一个使用new关键字创建对象的程序。
CreateObjectExample1.java
public class CreateObjectExample1 {
void show() {
System.out.println("Welcome to lidihuo");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating an object using new keyword
CreateObjectExample1 obj = new CreateObjectExample1();
//invoking method using the object
obj.show();
}
}
输出:
通过使用new关键字,我们还可以调用该类的构造函数(默认或参数化)。
CreateObjectExample2.java
public class CreateObjectExample2 {
CreateObjectExample2() {
System.out.println("Welcome to lidihuo");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating an object using new keyword
CreateObjectExample2 obj = new CreateObjectExample2();
}
}
输出:
使用clone()方法
clone()方法是
Object 类的方法。它创建一个对象的副本并返回相同的副本。调用clone()方法时,JVM 会创建一个新对象。它将先前创建的对象的所有内容复制到新的一个对象中。请注意,它不会调用任何构造函数。在使用clone()方法时,我们必须实现
Cloneable 接口。如果对象的类不支持Cloneable接口,则该方法将引发
CloneNotSupportedException 异常。如果无法克隆实例,则覆盖clone()方法的子类会引发异常。
注意: 该方法创建对象的副本,而不是新对象。
语法:
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
我们使用以下语句创建一个新对象。
ClassName newobject = (ClassName) oldobject.clone();
CreateObjectExample3.java
public class CreateObjectExample3 implements Cloneable
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
String str = "New Object Created";
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateObjectExample3 obj1 = new CreateObjectExample3();
try{
CreateObjectExample3 obj2 = (CreateObjectExample3) obj1.clone();
System.out.println(obj2.str);
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出:
使用Class类的newInstance()方法
Class类的
newInstance()方法也用于创建对象。它调用默认的构造函数来创建对象。它返回该对象表示的类的新创建实例。它在内部使用Constructor类的newInstance()方法。
语法:
public T newInstance() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException
它引发
IllegalAccessException,
InstantiationException,ExceptionInInitializerError 异常。
我们可以通过以下方式创建对象:
ClassName object = ClassName.class.newInstance();
或
ClassName object = (ClassName) Class.forName("fully qualified name of the class").newInstance();
在上面的语句中,
forName()是Class类的静态方法。它解析字符串类型的参数
className 。它返回具有完全限定名称的类的对象。它加载类,但不创建任何对象。如果无法加载类,则抛出
ClassNotFoundException ,如果链接失败,则抛出
LinkageError 。
要创建对象,我们使用
newInstance( )方法。仅当我们知道类的名称并且该类具有公共默认构造函数时,它才起作用。
在下面的程序中,我们使用newInstance()方法创建了一个新对象。
CreateObjectExample4.java
public class CreateObjectExample4 {
void show() {
System.out.println("A new object created.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
class cls = Class.forName("CreateObjectExample4");
CreateObjectExample4 obj = (CreateObjectExample4) cls.newInstance();
obj.show();
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出:
使用构造函数类的newInstance()方法
它与
Class 的
newInstance()方法相似类。这是创建对象的一种反射方式。该方法在
Constructor 类中定义,该类是
java.lang.reflect 包的类。我们还可以使用
newInstance()方法来调用参数化构造函数和私有构造函数。与Class类的
newInstance()方法相比,它是广泛首选的。
语法:
public T newInstance(Object... initargs) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
该方法将Objects数组解析为参数。包装在适当类型的包装对象中的基本类型的值。它返回通过调用构造函数创建的新对象。它会抛出
IllegalAccessException,IllegalArgumentException,InstantiationException,InvocationTargetException,ExceptionInInitializerError异常。
我们可以通过以下方式创建对象:
Constructor<
Employee>
constructor = Employee.class.getConstructor();
Employee emp3 = constructor.newInstance();
我们创建一个使用newInstance()方法创建对象的程序。
CreateObjectExample5.java
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public class CreateObjectExample5 {
private String str;
CreateObjectExample5() {
}
public void setName(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Constructor<
CreateObjectExample5>
constructor = CreateObjectExample5.class.getDeclaredConstructor();
CreateObjectExample5 r = constructor.newInstance();
r.setName("lidihuo");
System.out.println(r.str);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出:
使用反序列化
在Java中,
序列化是将对象转换为字节流序列的过程。序列化的反向过程(从字节流到对象)称为
反序列化。当我们序列化或反序列化一个对象时,JVM将创建一个新对象。它不使用构造函数来创建对象。使用反序列化时,必须在类中实现
Serializable 接口(标记接口)。
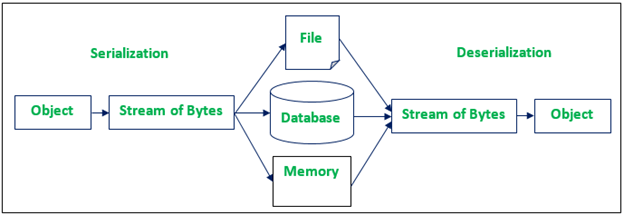
序列化
ObjectOutputStream 的
writeObject()方法类用于序列化对象。它将对象发送到输出流。
语法:
public final void writeObject(object x) throws IOException
反序列化:
ObjectInputStream 类的方法
readObject()用于反序列化对象。它从流中引用对象。
语法:
public final Object readObject() throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException
注意: 如果我们不想将字段包含为对象的一部分,则使字段为静态或瞬态。它不会包括在序列化过程中。
让我们了解通过程序进行的序列化和反序列化。
Employee.java
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Employee implements Serializable {
int empid;
String empname;
public Empoyee(int empid, String empname) {
this.empid = empid;
this.empname = empname;
}
}
我们创建了一个名为
Employee 的类,其对象将被序列化和反序列化。
Java对象的序列化:
在以下程序中,我们已使用ObjectOutputStream类的
writeObject()方法序列化了Employee类的对象。对象的状态保存在
employee.txt 文件中。
SerializationExample.java
import java.io.*;
class SerializationExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
Try{
//Creating the object
Employee emp = new Employee(198054,"Andrew");
//Creates a stream and writes the object
FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream("employee.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(employeeout);
out.writeObject(emp);
out.flush();
//closes the output stream
out.close();
System.out.println("Successfully Created");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
反序列化Java对象:
在以下程序中,我们将对在上述程序中序列化的对象进行反序列化。
DeserializationExample.java
import java.io.*;
class DeserializationExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
//Creating a stream to read the object
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("employee.txt"));
Employee e=(Employee)in.readObject();
//prints the data of the serialized object
System.out.println(e.empid+" "+e.empname);
//closing the input stream
in.close();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
在以上五个方法中,我们注意到
new 关键字和
newInstance()方法都使用构造函数创建对象,而其余两个方法都使用不使用构造函数。

