Java super关键字
Java中的
super 关键字是一个引用变量,用于引用直接父类对象。
每当创建子类的实例时,都会隐式创建父类的实例,该父类的实例由超级引用变量引用。
Java超级关键字的用法
super可用于引用直接父类实例变量。
super可用于调用直接父类方法。
super()可用于调用直接父类构造函数。

1)super用于请参考直接父类实例变量。
我们可以使用super关键字访问父类的数据成员或字段。如果父类和子类具有相同的字段,则使用它。
class Animal{
String color="white";
}
class Dog extends Animal{
String color="black";
void printColor(){
System.out.println(color);
//prints color of Dog classSystem.out.println(super.color);
//prints color of Animal class}
}
class TestSuper1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
d.printColor();
}
}
输出:
在上面的示例中,Animal和Dog这两个类具有相同的属性颜色。如果我们打印color属性,它将默认打印当前类的颜色。要访问父属性,我们需要使用super关键字。
2)super可用于调用父类方法
super关键字也可用于调用父类方法。如果子类包含与父类相同的方法,则应使用它。换句话说,如果方法被覆盖,则使用它。
class Animal{
void eat(){
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void eat(){
System.out.println("eating bread...");
}
void bark(){
System.out.println("barking...");
}
void work(){
super.eat();
bark();
}
}
class TestSuper2{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
d.work();
}
}
输出:
在上面的示例Animal和Dog中,如果我们从Dog类中调用eat()方法,则这两个类都具有eat()方法,默认情况下它将调用Dog类的eat()方法,因为优先级是local。
要调用父类方法,我们需要使用super关键字。
3)super用于调用父类构造函数。
super关键字也可以用于调用父类构造函数。让我们看一个简单的例子:
class Animal{
Animal(){
System.out.println("animal is created");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
Dog(){
super();
System.out.println("dog is created");
}
}
class TestSuper3{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
}
}
输出:
animal is createddog is created
注意: 如果没有super()或this(),super()会由编译器自动添加到每个类构造函数中。
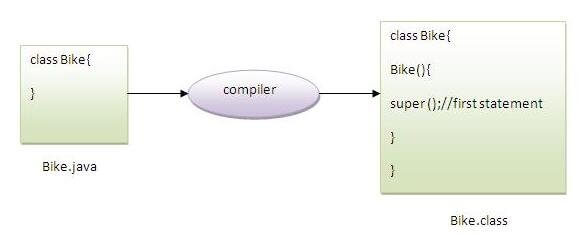
众所周知,如果存在默认构造函数,编译器会自动提供该默认构造函数不是构造函数。但是,它也将super()作为第一条语句添加。
super关键字的另一个示例,其中super()由编译器隐式提供。
class Animal{
Animal(){
System.out.println("animal is created");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
Dog(){
System.out.println("dog is created");
}
}
class TestSuper4{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
}
}
输出:
animal is createddog is created
超级示例: 实际使用
让我们看看超级关键字的实际使用。在这里,Emp类继承了Person类,因此默认情况下,Person的所有属性都将继承给Emp。为了初始化所有属性,我们使用子类的父类构造函数。这样,我们就可以重用父类的构造函数。
class Person{
int id;
String name;
Person(int id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
}
class Emp extends Person{
float salary;
Emp(int id,String name,float salary){
super(id,name);
//reusing parent constructorthis.salary=salary;
}
void display(){
System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+salary);
}
}
class TestSuper5{
public static void main(String[] args){
Emp e1=new Emp(1,"ankit",45000f);
e1.display();
}
}
输出:


