C++继承
在C++中,继承是一个过程,其中一个对象自动获取其父对象的所有属性和行为。这样,您就可以重用,扩展或修改在其他类中定义的属性和行为。
在C++中,继承另一个类的成员的类称为派生类,而该类的成员被继承的被称为基类。派生类是基类的专用类。
C++继承的优势
代码可重用性: 现在,您可以重用父类的成员了。因此,无需再次定义成员。因此,该类中所需的代码更少。
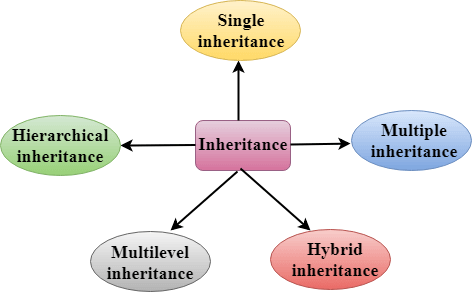
继承类型
C++支持五种继承类型:
单继承
multiset 继承
层次继承
多级继承
混合继承
派生类
派生类是定义为从基类派生的类。
派生类的语法:
class derived_class_name :: visibility-mode base_class_name
{
// body of the derived class.
}
位置
派生类名称: 这是派生类的名称。
可见性模式: 可见性模式指定基类的功能是公共继承的还是私有继承的。它可以是公共的或私有的。
base_class_name: 这是基类的名称。
当基类由派生类私有继承时,基类的公共成员将成为派生类的私有成员。因此,派生类的对象不能仅通过派生类的成员函数访问基类的公共成员。
当派生类公开继承基类时,基类的公共成员也将成为派生类的公共成员。因此,派生类的对象以及基类的成员函数都可以访问基类的公共成员。
注意:
在C++中,可见性的默认模式是private。
基类的私有成员永远不会被继承。
C++单一继承
单一继承被定义为从唯一的一个基类继承派生类的继承。
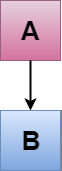
其中'A'是基类,'B'是派生类。
C++单级继承示例: 继承字段
当一个类继承另一类时,称为单级继承。让我们看一下仅继承字段的单级继承示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Account {
public:
float salary = 60000;
};
class Programmer: public Account {
public:
float bonus = 5000;
};
int main(void) {
Programmer p1;
cout<<"Salary: "<<p1.salary<<endl;
cout<<"Bonus: "<<p1.bonus<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
Salary: 60000
Bonus: 5000
在上面的示例中,Employee是 base 类,而Programmer是派生类。
C++单级继承示例: 继承方法
让我们看看C++中仅继承方法的继承示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout<<"Eating..."<<endl;
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void bark(){
cout<<"Barking...";
}
};
int main(void) {
Dog d1;
d1.eat();
d1.bark();
return 0;
}
输出:
让我们看一个简单的例子。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
int a = 4;
int b = 5;
public:
int mul()
{
int c = a*b;
return c;
}
};
class B : private A
{
public:
void display()
{
int result = mul();
std::cout <<"Multiplication of a and b is : "<<result<< std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
b.display();
return 0;
}
输出:
Multiplication of a and b is : 20
在上面的示例中,类A是私有继承的。因此,类'A'的mul()函数不能由类B的对象访问。只能由类B的成员函数访问。
如何制作私有成员可继承
私有成员不可继承。如果我们通过公开公开来修改可见性模式,但这会剥夺数据隐藏的优势。
C++引入了第三个可见性修改器,即受保护的。声明为受保护的成员将可用于该类中的所有成员函数以及从其直接派生的类。
可见性模式可分为三类:
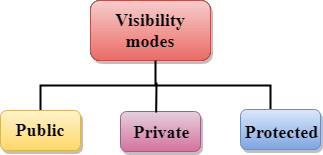 公共: 将成员声明为公共成员后,该程序的所有功能都可以访问。
私有: 将成员声明为私有成员后,只能在该类中访问。
受保护的: 将成员声明为受保护成员后,就可以在其自己的类以及从其派生的类中对其进行访问。
公共: 将成员声明为公共成员后,该程序的所有功能都可以访问。
私有: 将成员声明为私有成员后,只能在该类中访问。
受保护的: 将成员声明为受保护成员后,就可以在其自己的类以及从其派生的类中对其进行访问。
继承的成员的可见性
| Private |
派生的类可见性 |
| Public |
Private |
Protected |
| Private |
不能继承 |
不能继承 |
不能继承 |
| Protected |
Protected |
Private |
Protected |
| Public |
Public |
Private |
Protected |
C++多级继承
多级继承是从另一个派生类派生一个类的过程。

C++多级继承示例
当一个类继承另一类时进一步被另一个类继承,在C++中被称为多级继承。继承是可传递的,因此last派生类将获取其所有基类的所有成员。
让我们看看C++中多级继承的示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout<<"Eating..."<<endl;
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void bark(){
cout<<"Barking..."<<endl;
}
};
class BabyDog: public Dog
{
public:
void weep() {
cout<<"Weeping...";
}
};
int main(void) {
BabyDog d1;
d1.eat();
d1.bark();
d1.weep();
return 0;
}
输出:
Eating...
Barking...
Weeping...
C++ multiset 继承
multiset 继承是派生一个新类的过程,该类继承了两个或多个类的属性。
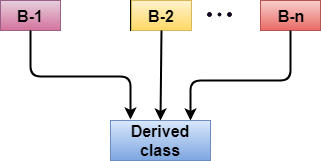
派生类的语法:
class D : visibility B-1, visibility B-2, ?
{
// Body of the class;
}
让我们看一个简单的 multiset 继承示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int a;
public:
void get_a(int n)
{
a = n;
}
};
class B
{
protected:
int b;
public:
void get_b(int n)
{
b = n;
}
};
class C : public A,public B
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "The value of a is : " <<a<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The value of b is : " <<b<< std::endl;
cout<<"Addition of a and b is : "<<a+b;
}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.get_a(10);
c.get_b(20);
c.display();
return 0;
}
输出:
The value of a is : 10
The value of b is : 20
Addition of a and b is : 30
在上面的示例中,类'C'在公共模式下继承了两个基类'A'和'B'。
继承中的泛型解析
当一个同名的函数出现在多个基类中时,使用 multiset 继承会出现歧义。
让我们通过一个例子来理解这一点:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "class A" << std::endl;
}
};
class B
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "class B" << std::endl;
}
};
class C : public A, public B
{
void view()
{
display();
}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.display();
return 0;
}
输出:
error: reference to 'display' is ambiguous
display();
上述问题可以通过将类解析运算符与函数一起使用来解决。在上面的示例中,派生的类代码可以重写为:
class C : public A, public B
{
void view()
{
A :: display(); // Calling the display() function of class A.
B :: display(); // Calling the display() function of class B.
}
};
在单个继承中也可能出现歧义。
请考虑以下情况:
class A
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<?class A?;
}
} ;
class B
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<?class B?;
}
} ;
在上述情况下,派生类的功能将覆盖基类的方法。因此,调用display()函数将只调用派生类中定义的函数。如果要调用基类函数,则可以使用类解析运算符。
int main()
{
B b;
b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class.
b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class.
}
C++混合继承
混合继承是一种以上继承的组合。

让我们看一个简单的示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int a;
public:
void get_a()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of 'a' : " << std::endl;
cin>>a;
}
};
class B : public A
{
protected:
int b;
public:
void get_b()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of 'b' : " << std::endl;
cin>>b;
}
};
class C
{
protected:
int c;
public:
void get_c()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of c is : " << std::endl;
cin>>c;
}
};
class D : public B, public C
{
protected:
int d;
public:
void mul()
{
get_a();
get_b();
get_c();
std::cout << "Multiplication of a,b,c is : " <<a*b*c<< std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D d;
d.mul();
return 0;
}
输出:
Enter the value of 'a' :
10
Enter the value of 'b' :
20
Enter the value of c is :
30
Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000
C++层次继承
层次继承定义为从基类派生多个类的过程。
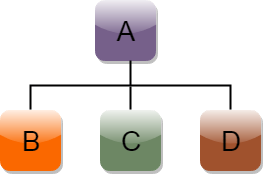
分层继承的语法:
class A
{
// body of the class A.
}
class B : public A
{
// body of class B.
}
class C : public A
{
// body of class C.
}
class D : public A
{
// body of class D.
}
让我们看一个简单的例子:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape // Declaration of base class.
{
public:
int a;
int b;
void get_data(int n,int m)
{
a= n;
b = m;
}
};
class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class
{
public:
int rect_area()
{
int result = a*b;
return result;
}
};
class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class
{
public:
int triangle_area()
{
float result = 0.5*a*b;
return result;
}
};
int main()
{
Rectangle r;
Triangle t;
int length,breadth,base,height;
std::cout << "Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: " << std::endl;
cin>>length>>breadth;
r.get_data(length,breadth);
int m = r.rect_area();
std::cout << "Area of the rectangle is : " <<m<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Enter the base and height of the triangle: " << std::endl;
cin>>base>>height;
t.get_data(base,height);
float n = t.triangle_area();
std::cout <<"Area of the triangle is : " << n<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle:
23
20
Area of the rectangle is : 460
Enter the base and height of the triangle:
2
5
Area of the triangle is : 5



 公共: 将成员声明为公共成员后,该程序的所有功能都可以访问。
私有: 将成员声明为私有成员后,只能在该类中访问。
受保护的: 将成员声明为受保护成员后,就可以在其自己的类以及从其派生的类中对其进行访问。
公共: 将成员声明为公共成员后,该程序的所有功能都可以访问。
私有: 将成员声明为私有成员后,只能在该类中访问。
受保护的: 将成员声明为受保护成员后,就可以在其自己的类以及从其派生的类中对其进行访问。



