Ruby 日期和时间
Ruby 日期和时间
Ruby 在其文档中主要包含三个与日期和时间相关的类。
Date
DateTime
Time
Date
Ruby date 提供了两个类,Date 和DateTime。
要理解日期的概念,首先我们需要了解一些术语。
Calendar date: 日历日期是一年中某个日历月内的特定日期。
Ordinal date: 序数日期是由其序数标识的日历年中的特定日期。
Week date: 周日期是由日历周和天数标识的日期。一年中的第一个日历周包括该年的第一个星期四。
Julian day number: 儒略日数是自公元前 4713 年 1 月 1 日中午以来经过的一天。
Modified julian day number: 修改后的儒略日数是自公元 1858 年 11 月 17 日午夜以来经过的一天。
Date 对象是用 ::new、::parse、::today、::jd、::strptime 等创建的。所有日期对象都是不可变的,因此它们不能修改自己。
示例:
require 'date'
puts Date.new(2017,4,3)
puts Date.jd(2451877)
puts Date.ordinal(2017,3)
puts Date.commercial(2017,5,6)
puts Date.parse('2017-02-03')
puts Date.strptime('03-02-2017', '%d-%m-%Y')
puts Time.new(2017,10,8).to_date
输出:
Date 对象有如下所示的各种方法在下面的例子中。
例子:
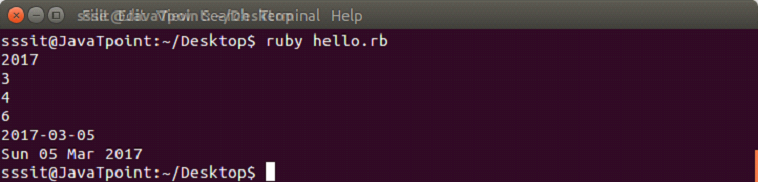
require 'date'
d = Date.parse('4th Mar 2017')
puts d.year
puts d.mon
puts d.mday
puts d.wday
puts d += 1
puts d.strftime('%a %d %b %Y')
输出:
DateTime
Ruby DateTime 是 Date 的子类。它可以轻松处理日期、小时、分钟、秒和偏移量。
使用 DateTime.new、DateTime.ordinal、DateTime.parse、DateTime.jd、DateTime.commercial、DateTime.now 等创建的 DateTime 对象.
示例:
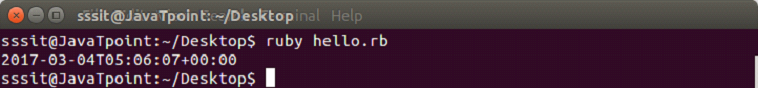
require 'date'
puts DateTime.new(2017,3,4,5,6,7)
输出:
日、分的最后一个元素,秒或小时可以是小数。
DateTime 对象具有多种方法,如下例所示。
示例:
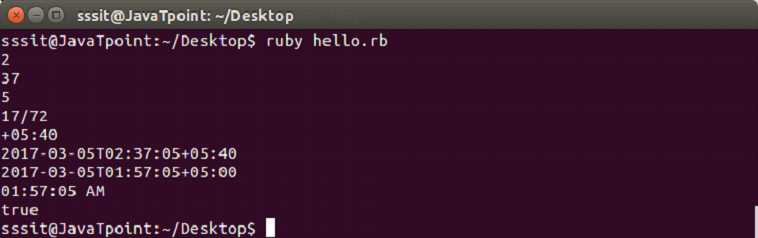
require 'date'
d = DateTime.parse('4th Mar 2017 02:37:05+05:40')
puts d.hour
puts d.min
puts d.sec
puts d.offset
puts d.zone
puts d += Rational('1.0')
puts d = d.new_offset('+05:00')
puts d.strftime('%I:%M:%S %p')
puts d > DateTime.new(2000)
输出:
Time
Time 类是日期和时间的抽象。它在内部存储为自纪元时间以来的秒数。 Time 类将 GMT(格林威治标准时间)和 UTC(协调世界时)视为等价的。
时间可能看起来相等,但经过比较它们可能不同,因为所有时间都可能有分数。
Time 实现使用有符号的 63 位整数,Bignum 或 Rational。使用整数时,时间会变慢。
创建新的时间实例
可以使用 ::new 创建新的时间实例。这将使用您当前系统的时间。也可以传递年、月、日、小时、分钟等部分时间。
在创建新时间实例时,您至少需要传递一年。如果仅传递年份,则时间将默认为该年的 1 月 1 日 00:00:00,使用当前系统时区。
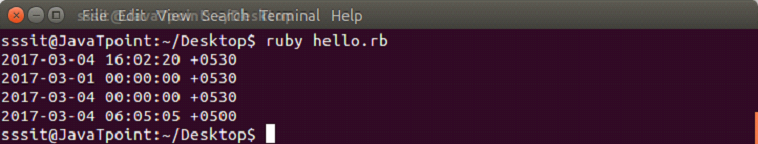
示例:
puts Time.new
puts Time.new(2017, 3)
puts Time.new(2017, 3, 4)
puts Time.new(2017, 3, 4, 6, 5, 5, "+05:00")
输出:
使用 gm、utc 和本地函数的时间
除了使用当前系统设置,您还可以使用 GMT、本地和 UTC 时区。
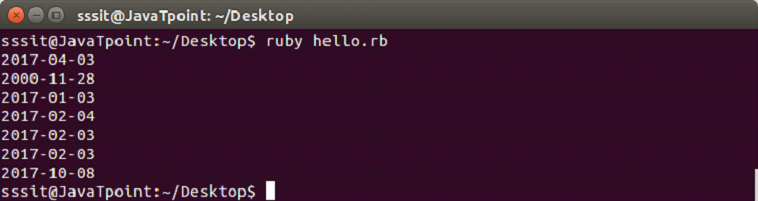
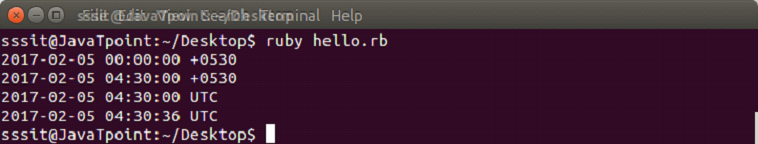
示例:
puts Time.local(2017, 2, 5)
puts Time.local(2017, 2, 5, 4, 30)
puts Time.utc(2017, 2, 5, 4, 30)
puts Time.gm(2017, 2, 5, 4, 30, 36)
输出:
使用时间实例
创建时间实例后,我们可以通过以下方式处理该时间。
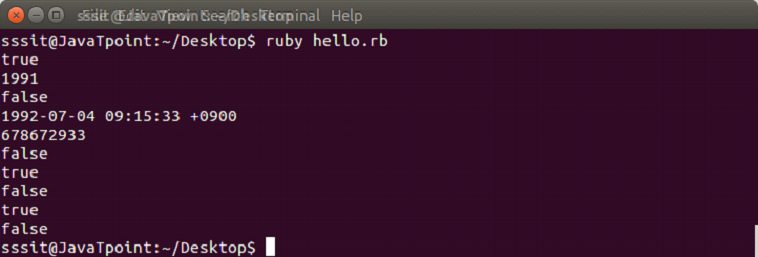
示例:
t = Time.new(1991, 07, 5, 9, 15, 33, "+09:00")
puts t.friday? #=> false
puts t.year #=> 1993
puts t.dst? #=> false
puts t + (60*60*24*365) #=> 1994-02-24 12:00:00 +0900
puts t.to_i #=> 730522800
t1 = Time.new(2017)
t2 = Time.new(2015)
puts t1 == t2 #=> false
puts t1 == t1 #=> true
puts t1 < t2 #=> true
puts t1 > t2 #=> false
puts Time.new(2010,10,31).between?(t1, t2) #=> true
输出:
时区和夏令时
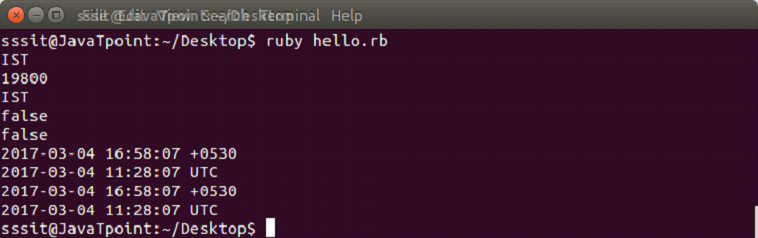
Time 对象可用于获取与时区相关的所有信息。所有信息将根据我们系统的当前时间显示。
示例:
time = Time.new
puts time.zone
puts time.utc_offset
puts time.zone
puts time.isdst
puts time.utc?
puts time.localtime
puts time.gmtime
puts time.getlocal
puts time.getutc
输出: