ES6 类
ES6 类
类是面向对象编程(OOP) 的重要组成部分。类用于定义现实世界对象建模的蓝图,并将代码组织成可重用的逻辑部分。
在 ES6 之前,很难在 JavaScript。但是在 ES6 中,我们可以使用 class 关键字来创建类。我们可以通过类表达式或使用类声明在代码中包含类。
类定义只能包含构造函数和函数。这些组件统称为类的数据成员。类包含为类的对象分配内存的构造函数。类包含负责对对象执行操作的函数。
注意: 类的主体只包含方法,而不是数据属性。
语法: 类表达式
var var_name = new class_name {
}
语法: 类声明
让我们看看类表达式和类声明的插图。
示例-类声明
class Student{
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
示例-类表达式
var Student = class{
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
从类实例化一个对象
像其他面向对象的编程语言一样,我们可以使用 new 关键字从类实例化一个对象。
语法
var obj_name = new class_name([arguements])
示例
var stu = new Student('Peter', 22)
访问函数
对象可以访问类的属性和函数。我们使用 '.'点符号(或句点)用于访问类的数据成员。
语法
示例
'use strict'
class Student {
constructor(name, age) {
this.n = name;
this.a = age;
}
stu() {
console.log("The Name of the student is: ", this.n)
console.log("The Age of the student is: ",this. a)
}
}
var stuObj = new Student('Peter',20);
stuObj.stu();
在上面的例子中,我们声明了一个类Student。该类的构造函数分别包含两个参数name 和age。关键字 'this' 指的是类的当前实例。我们也可以说上面的构造函数初始化了两个变量'n'和'a'以及传递给构造函数的参数值。
函数stu() 在类中将打印name和age的值。
输出
The Name of the student is: Peter
The Age of the student is: 20
注意: 在类中必须包含构造函数定义,因为默认情况下,每个类都有一个构造函数。
Static 关键字
static 关键字用于制作类中的静态函数。静态函数只能通过类名引用。
示例
'use strict'
class Example {
static show() {
console.log("static Function")
}
}
Example.show() //invoke the static method
输出
类继承
在ES6之前,继承的实现需要几个脚步。但是 ES6 通过使用 extends 和 super 关键字简化了继承的实现。
继承是从现有实体创建新实体的能力。为创建新类而扩展的类称为超类/父类,而新创建的类称为子类/子类。
一个类可以通过使用'extends' 关键字从另一个类继承。除了父类的构造函数,子类继承所有的属性和方法。
语法
class child_class_name extends parent_class_name{
}
一个类使用extends关键字从另一个类继承。
示例
'use strict'
class Student {
constructor(a) {
this.name = a;
}
}
class User extends Student {
show() {
console.log("The name of the student is: "+this.name)
}
}
var obj = new User('Sahil');
obj.show()
在上面的例子中,我们声明了一个类student。通过使用extends 关键字,我们可以创建一个新类User,该类与其父类Student 具有相同的特征。所以,我们可以看出这些类之间存在继承关系。
输出
The name of the student is: Sahil
继承的类型
继承可以分为单级继承、多级继承和多级继承。 ES6 不支持多重继承。
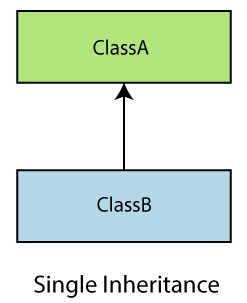
单级继承
定义为派生类只能从一个基类继承的继承班级。它允许派生类继承基类的行为和属性,从而实现代码的可重用性以及向现有代码添加新功能。
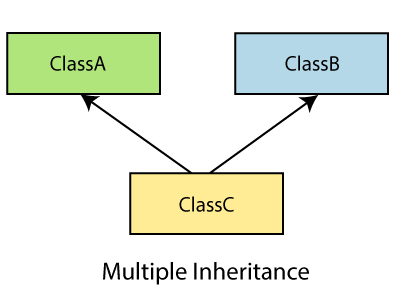
多重继承
在多重继承中,一个类可以从多个类继承。
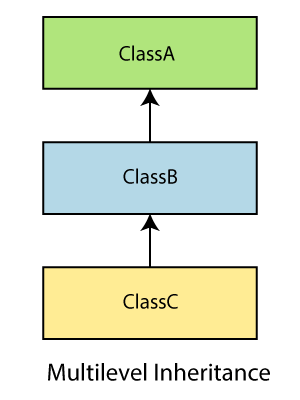
多级继承
在多级继承中,派生类是从另一个派生类创建的。因此,多级继承有多个父类。
让我们了解一下使用以下示例。
示例
class Animal{
eat(){
console.log("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
bark(){
console.log("barking...");
}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog{
weep(){
console.log("weeping...");
}
}
var d=new BabyDog();
d.eat();
d.bark();
d.weep();
输出
eating...
barking...
weeping...
方法覆盖和继承
该功能允许子类提供其父类已经提供的方法的特定实现。
为方法覆盖定义了一些规则-
方法名称必须与父类中的相同。
方法签名必须与父类中的相同。
让我们试着理解同样的插图:
例子
'use strict' ;
class Parent {
show() {
console.log("It is the show() method from the parent class");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
show() {
console.log("It is the show() method from the child class");
}
}
var obj = new Child();
obj.show();
在上面的例子中,父类函数的实现在子类中发生了变化。上面代码执行成功后会得到如下输出:
输出
It is the show() method from the child class
super 关键字
它允许子类调用直接父类的属性、方法和构造函数。它是在 ECMAScript 2015 或 ES6 中引入的。 super.prop 和 super[expr] 表达式在对象字面量和类中的任何方法的定义中都是可读的。
语法
super(arguments);
例子
在这个例子中,父类的特性已经扩展到了它的子类。这两个类都有其独特的属性。在这里,我们使用 super 关键字来访问从父类到子类的属性。
'use strict' ;
class Parent {
show() {
console.log("It is the show() method from the parent class");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
show() {
super.show();
console.log("It is the show() method from the child class");
}
}
var obj = new Child();
obj.show();
输出
It is the show() method from the parent class
It is the show() method from the child class



