C语言Switch
C中的switch语句是if-else-if梯形语句的替代,它允许我们对单个变量的不同可能值执行多项操作。称为Switch变量。在这里,我们可以针对单个变量的不同值在多种情况下定义各种语句。
如下:
switch(expression){
case value1:
//code to be executed;
break; //optional
case value2:
//code to be executed;
break; //optional
......
default:
code to be executed if all cases are not matched;
}
C语言中的switch语句规则
1)
switch表达式必须为整数或字符类型。
2)
case值必须是整数或字符常量。
3)
case值仅可在switch语句内使用。
4)切换情况下的
break语句不是必须的。它是可选的。如果在该案例中未找到break语句,则所有案例将在匹配的案例之后执行。称为
掉线 CSwitch语句的状态。
让我们尝试通过示例来理解它。我们假设存在以下变量。
int x,y,z;
char a,b;
float f;
| Valid Switch |
Invalid Switch |
Valid Case |
Invalid Case |
| switch(x) |
switch(f) |
case 3; |
case 2.5; |
| switch(x>y) |
switch(x+2.5) |
case 'a'; |
case x; |
| switch(a+b-2) |
|
case 1+2; |
case x+2; |
| switch(func(x,y)) |
|
case 'x'>'y'; |
case 1,2,3; |
C中switch语句的流程图
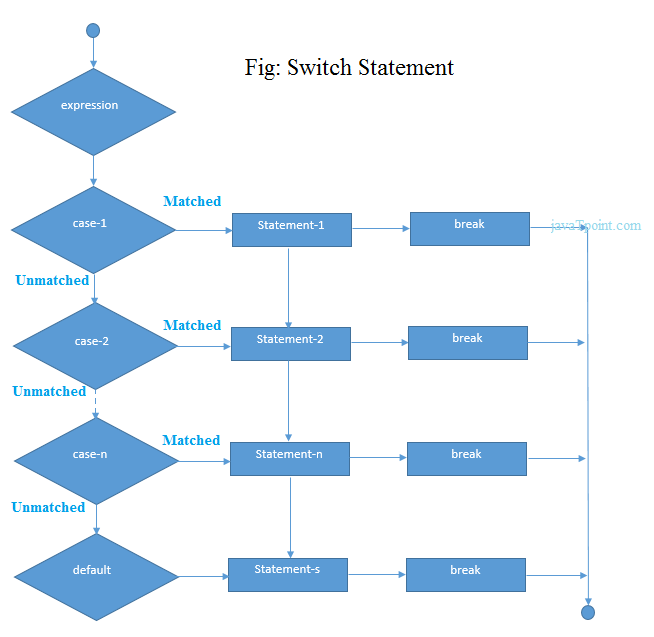
switch case语句的功能
首先,对switch语句中指定的整数表达式进行求值。然后将该值与在不同情况下给出的常数一一匹配。如果找到匹配项,则将执行该情况下指定的所有语句以及该情况之后的所有所有情况(包括默认语句)。没有两种情况可以具有相似的值。如果匹配的案例包含一个break语句,则将跳过此之后存在的所有案例,并且控件脱离Switch。否则,将执行匹配大小写之后的所有大小写。
让我们看一个简单的c语言switch语句示例。
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int number=0;
printf("enter a number:");
scanf("%d",&number);
switch(number){
case 10:
printf("number is equals to 10");
break;
case 50:
printf("number is equal to 50");
break;
case 100:
printf("number is equal to 100");
break;
default:
printf("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
}
return 0;
}
输出
enter a number:4
number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
enter a number:50
number is equal to 50
切换案例示例2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 10, y = 5;
switch(x>y && x+y>0)
{
case 1:
printf("hi");
break;
case 0:
printf("bye");
break;
default:
printf(" Hello bye ");
}
}
输出
C Switch语句是直通的
在C语言中,switch语句是直通的;这意味着如果您在switch案例中不使用break语句,则匹配案例之后的所有案例都将被执行。
让我们尝试通过以下示例了解switch语句的失败状态
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int number=0;
printf("enter a number:");
scanf("%d",&number);
switch(number){
case 10:
printf("number is equal to 10\n");
case 50:
printf("number is equal to 50\n");
case 100:
printf("number is equal to 100\n");
default:
printf("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
}
return 0;
}
输出
enter a number:10
number is equal to 10
number is equal to 50
number is equal to 100
number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
输出
enter a number:50
number is equal to 50
number is equal to 100
number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
嵌套的切换案例语句
我们可以在switch语句中使用任意数量的switch语句。这种类型的语句称为嵌套切换案例语句。请考虑以下示例。
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int i = 10;
int j = 20;
switch(i) {
case 10:
printf("the value of i evaluated in outer switch: %d\n",i);
case 20:
switch(j) {
case 20:
printf("The value of j evaluated in nested switch: %d\n",j);
}
}
printf("Exact value of i is : %d\n", i );
printf("Exact value of j is : %d\n", j );
return 0;
}
输出
the value of i evaluated in outer switch: 10
The value of j evaluated in nested switch: 20
Exact value of i is : 10
Exact value of j is : 20

