哈希表
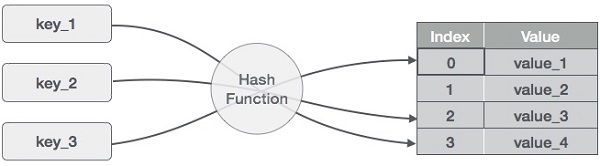
哈希表是一种以关联方式存储数据的数据结构。在哈希表中,数据以数组格式存储,其中每个数据值都有自己唯一的索引值。如果我们知道所需数据的索引,数据的访问将变得非常快。
因此,它成为一种数据结构,无论数据大小如何,插入和搜索操作都非常快。哈希表以数组为存储介质,利用哈希技术生成要插入或定位元素的索引。
散列
散列是一种将键值范围转换为数组索引范围的技术。我们将使用模运算符来获取一系列键值。考虑一个大小为 20 的哈希表的示例,并且要存储以下项目。项目采用(键,值)格式。
 (1,20)
(2,70)
(42,80)
(4,25)
(12,44)
(14,32)
(17,11)
(13,78)
(37,98)
(1,20)
(2,70)
(42,80)
(4,25)
(12,44)
(14,32)
(17,11)
(13,78)
(37,98)
| 键 |
哈希 |
数组索引 |
| 1 |
1 % 20 = 1 |
1 |
| 2 |
2 % 20 = 2 |
2 |
| 42 |
42 % 20 = 2 |
2 |
| 4 |
4 % 20 = 4 |
4 |
| 12 |
12 % 20 = 12 |
12 |
| 14 |
14 % 20 = 14 |
14 |
| 17 |
17 % 20 = 17 |
17 |
| 13 |
13 % 20 = 13 |
13 |
| 37 |
37 % 20 = 17 |
17 |
线性探测
如我们所见,散列技术可能会用于创建已使用的数组索引。在这种情况下,我们可以通过查看下一个单元格来搜索数组中的下一个空位置,直到找到一个空单元格。这种技术称为线性探测。
| 键 |
哈希 |
数组索引 |
线性探测后,数组索引 |
| 1 |
1 % 20 = 1 |
1 |
1 |
| 2 |
2 % 20 = 2 |
2 |
2 |
| 42 |
42 % 20 = 2 |
2 |
3 |
| 4 |
4 % 20 = 4 |
4 |
4 |
| 12 |
12 % 20 = 12 |
12 |
12 |
| 14 |
14 % 20 = 14 |
14 |
14 |
| 17 |
17 % 20 = 17 |
17 |
17 |
| 13 |
13 % 20 = 13 |
13 |
13 |
| 37 |
37 % 20 = 17 |
17 |
18 |
基本操作
以下是哈希表的基本主要操作。
Search-搜索哈希表中的元素。
Insert-在哈希表中插入一个元素。
delete-从哈希表中删除一个元素。
数据项
定义一个包含一些数据和键的数据项,基于它在哈希表中进行搜索。
struct DataItem {
int data;
int key;
};
Hash方法
定义一个散列方法来计算数据项的键的散列码。
int hashCode(int key){
return key % SIZE;
}
Search操作
每当要搜索一个元素时,计算传递的键的哈希码并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位该元素。如果在计算的哈希码中找不到元素,则使用线性探测来获取元素。
示例
struct DataItem *search(int key) {
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != null) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
Insert操作
每当要插入一个元素时,计算传递的键的哈希码并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位索引。如果在计算的哈希码中找到元素,则对空位置使用线性探测。
示例
void insert(int key,int data) {
struct DataItem *item = (struct DataItem*) malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
item->data = data;
item->key = key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty or deleted cell
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != null && hashArray[hashIndex]->key !=-1) {
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
hashArray[hashIndex] = item;
}
删除操作
每当要删除一个元素时,计算传递的键的哈希码并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位索引。如果在计算的哈希码中找不到元素,则使用线性探测来获取元素。找到后,在其中存储一个虚拟项目以保持哈希表的性能不变。
示例
struct DataItem* delete(struct DataItem* item) {
int key = item->key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] !=NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
struct DataItem* temp = hashArray[hashIndex];
//assign a dummy item at deleted position
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem;
return temp;
}
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}

 (1,20)
(2,70)
(42,80)
(4,25)
(12,44)
(14,32)
(17,11)
(13,78)
(37,98)
(1,20)
(2,70)
(42,80)
(4,25)
(12,44)
(14,32)
(17,11)
(13,78)
(37,98)