CSS content
此CSS属性会生成动态内容。它可以与伪元素
::before 和
::after 一起使用。所有浏览器均完全支持此CSS属性,该CSS属性用于将生成的内容插入网页中。
它将元素替换为生成的值。
语法
content: normal | none | counter | string | attr | open-quote | close-quote | no-close-quote | no-open-quote | url | initial | inherit;
属性值
此
CSS 属性具有许多值,它们分别是定义如下表:
| 值 |
说明 |
| normal |
用于设置默认值 |
| none |
此值不会设置内容。 |
| counter |
它将内容设置为计数器。通常是一个数字。使用 counter()或 counters()函数显示。 |
| string |
它用于设置任何字符串值。它应始终用引号引起来。它会在HTML元素之后或之前生成任何字符串。 |
| attr |
它将在元素之后或之前插入指定属性的值。如果选择器没有特定属性,则将插入一个空字符串。 |
| open-quote |
用于插入引号,或将内容设置为引号。 |
| close-quote |
用于插入右引号,或将内容设置为右引号。 |
| no-close-quote |
如果指定了右引号,则用于从内容中删除右引号。 |
| no-open-quote |
如果指定了开头引号,则用于从内容中删除开头引号。 |
| url |
它用于将内容设置为某些媒体,可以是图像,视频,音频等等。 |
| initial |
用于将属性设置为其默认值。 |
| inherit |
它从其父元素继承属性。 |
我们看看此CSS属性的一些说明。
示例-使用
normal 和
none 值
在此示例中,我们使用
:: before 伪元素在段落元素之前插入文本
" Welcome" 。文本不会被添加到我们在其中应用了
normal 和
none 值的那些段落元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS content Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-size: 25px;
}
p::before {
content: "Welcome ";
}
#para::before {
content: normal;
}
#para1::before {
content: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> CSS content property </h1>
<h2> Use of content: normal; and content: none; </h2>
<p> to the lidihuo.com </p>
<p id="para"> This is a paragraph using <b>normal</b> value. </p>
<p id="para1"> This is another paragraph using <b>none</b> value. </p>
</body>
</html>
输出

示例-使用
string和
url 值
在此示例中,文本
" Hello World。Welcome" 通过使用content属性和
:: before 伪元素添加。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS content Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-size: 25px;
}
p::before {
content: "Hello World. Welcome ";
}
#para::before {
content: url("https://www.lidihuo.com/images/icon3.png");
}
#para1::before {
content: url("https://www.lidihuo.com/images/icon3.png");
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> CSS content property </h1>
<h2> Use of content: string; and content: url(); </h2>
<p> to the lidihuo.com </p>
<p id="para"> This is a paragraph using the <b>url()</b> value. </p>
<p id="para1"> This is another paragraph using the <b>url()</b> value. </p>
</body>
</html>
输出

示例-使用
open-quote和
close-quote值
如果不使用
close-quote,我们将无法应用
open-quote。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS content Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-size: 25px;
}
p::before {
content: open-quote;
}
p::after {
content: close-quote;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> CSS content property </h1>
<h2> Use of content: open-quote; and content: close-quote; </h2>
<p> Welcome to the lidihuo.com </p>
<p> This is another paragraph. </p>
</body>
</html>
输出

示例-使用
no-open-quote和
no-close-quote值
在此示例中,我们应用了在段落元素上,以及在类别为
.para 的段落上,使用
no-open-quote 和
close-quote 。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-size: 25px;
}
p::before {
content: open-quote;
}
p::after {
content: close-quote;
}
p.para::before {
content: no-open-quote;
}
p.para::after {
content: no-close-quote;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> CSS content property </h1>
<h2> Use of content: no-open-quote; and content: no-close-quote; </h2>
<p> Welcome to the lidihuo.com </p>
<p class="para"> This is another paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
输出

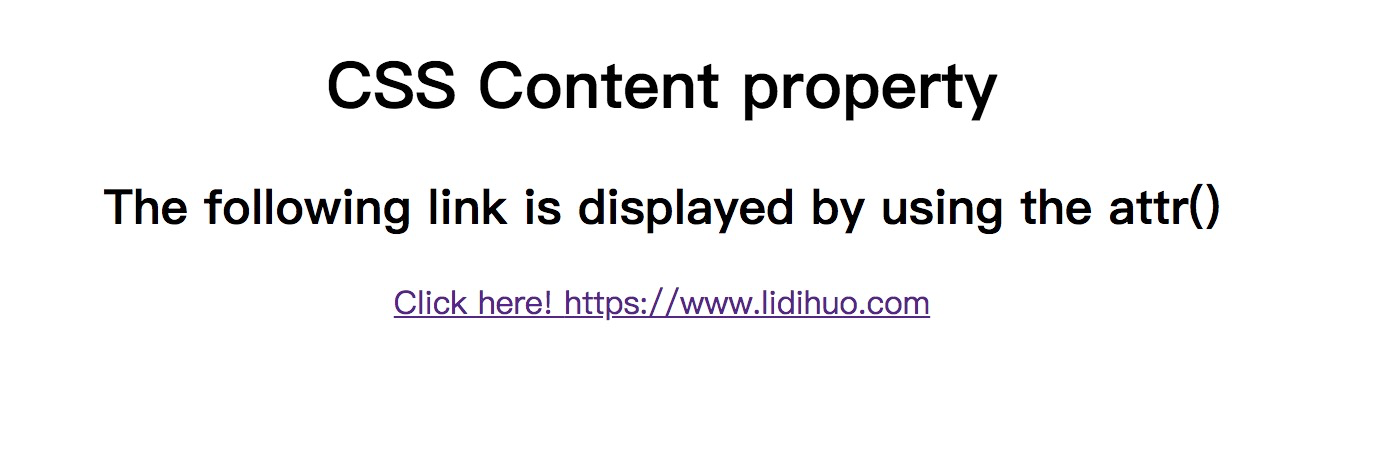
示例-使用
attr()
attr()函数允许我们插入特定属性的值。如果相应的元素没有属性,则将返回一个空字符串。
在此示例中,屏幕上显示的链接是使用
attr()函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS content Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
}
a::after {
content: attr(href);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> CSS Content property </h1>
<h2> The following link is displayed by using the <b>attr()</b> </h2>
<a href=https://www.lidihuo.com>Click here! </a>
</body>
</html>
输出